Understanding Low Voltage Motor: Applications, Control, and Performance
Introduction to Low Voltage Motors
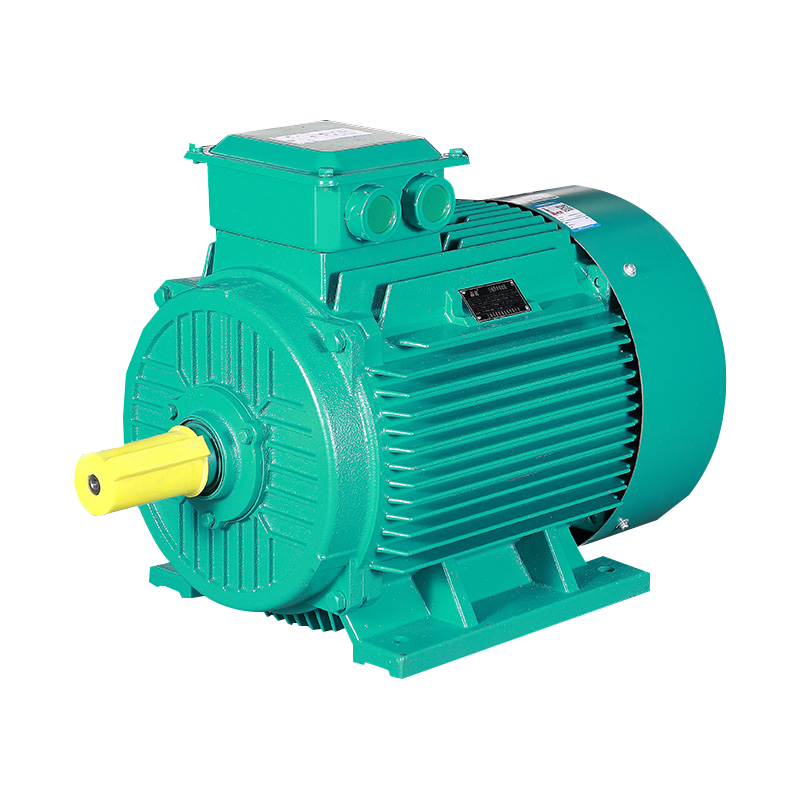
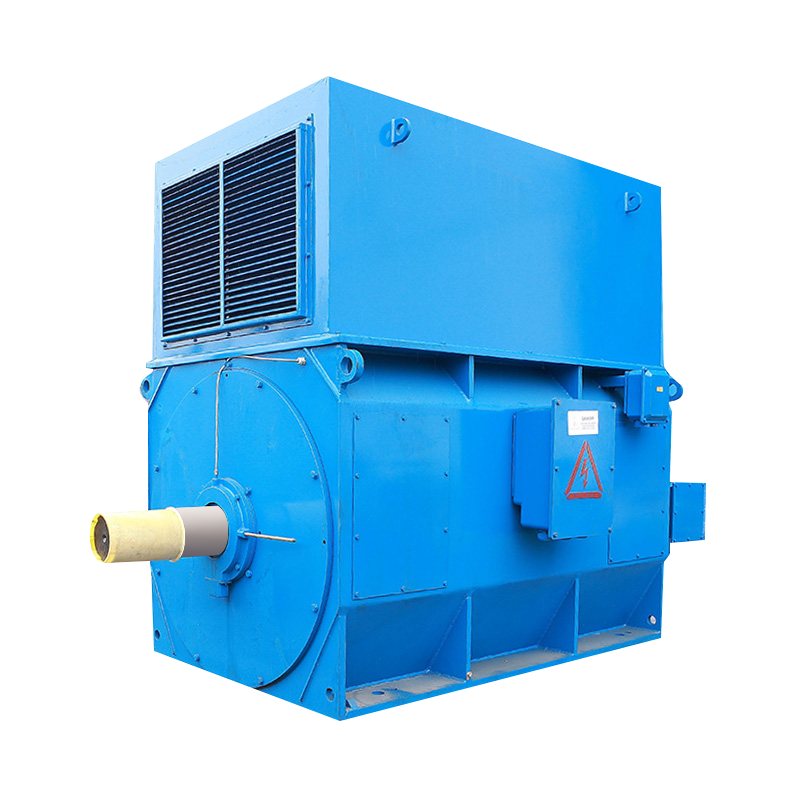
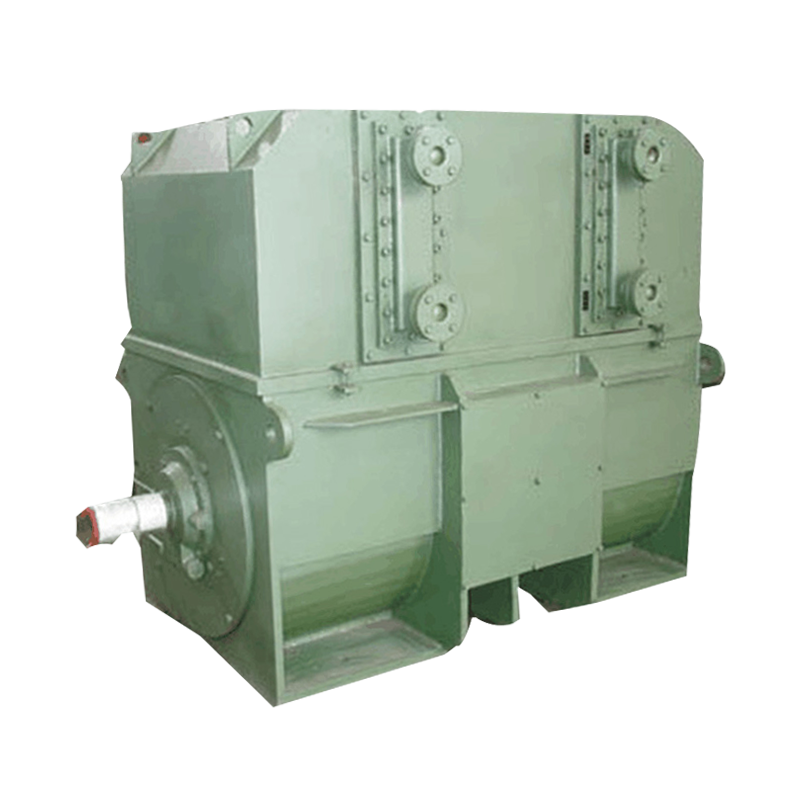
Low voltage motors are electrical machines designed to operate at a voltage typically below 1000V for AC motors and below 120V for DC motors. These motors are widely used in industrial, commercial, and residential applications where safety, energy efficiency, and compact design are essential. Unlike high voltage motors, low voltage motors offer easier installation, reduced insulation requirements, and safer handling for operators and maintenance personnel.
One of the primary advantages of low voltage motors is their suitability for low-power and sensitive applications. They are commonly used in automation systems, robotics, HVAC units, pumps, fans, and small machinery. Their lower voltage operation reduces the risk of electrical hazards while still providing adequate performance for a variety of tasks.
Low voltage motors are typically smaller in size, which allows for more flexible integration into equipment and machinery. Despite their compact design, advancements in motor technology have ensured that they maintain reliable performance, energy efficiency, and long operational life. Modern low voltage motors are engineered to deliver consistent torque and speed while minimizing energy losses.
In addition to safety and compactness, low voltage motors contribute to energy savings in applications where continuous operation is required. Their efficiency can be further enhanced through proper motor selection, load matching, and implementation of effective control techniques such as variable frequency drives or pulse width modulation.
Overall, low voltage motors provide a balanced combination of safety, efficiency, and versatility. They form the backbone of many electrical systems where reliable, low-power operation is necessary, making them an essential component in modern industrial, commercial, and residential environments.
Low Voltage DC Motor Applications
Low voltage DC motors are widely used in applications where precise control, compact size, and safety are critical. They are particularly suitable for devices that require variable speed, consistent torque, and energy-efficient operation. Common applications include automation systems, robotics, small machinery, pumps, fans, and household appliances.
In industrial automation, low voltage DC motors are employed to drive conveyors, actuators, and robotic arms. Their ability to provide smooth start and stop operations, combined with easy speed control, makes them ideal for precise mechanical tasks. In the commercial and residential sectors, these motors are often used in HVAC systems, electric doors, and small appliances, offering quiet and efficient operation.
One of the advantages of low voltage DC motors is their adaptability to control techniques such as Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), which allows for fine speed adjustments and energy savings. Additionally, these motors are safer to handle due to their lower operating voltage, reducing the risk of electrical shock or insulation failure.
Typical Low Voltage DC Motor Applications and Parameters
| Application | Voltage Range | Typical Power | Speed Range | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Robotics and Automation | 12V–48V | 10–200W | 500–5000 RPM | Precise speed and torque control |
| Pumps and Fans | 24V–48V | 50–500W | 1000–3000 RPM | Efficient continuous operation |
| HVAC and Appliances | 12V–24V | 20–300W | 800–4000 RPM | Quiet and compact design |
| Electric Doors and Actuators | 12V–36V | 30–150W | 500–2000 RPM | Reliable start/stop and low maintenance |
Low Voltage Motor Control Techniques
Effective control of low voltage motors is essential for optimizing performance, efficiency, and lifespan. Control techniques regulate speed, torque, and direction of rotation, allowing motors to perform precise and reliable operations in industrial, commercial, and residential applications.
Common Control Methods
Several control methods are commonly applied to low voltage motors, each with its advantages depending on the application:
- Pulse Width Modulation (PWM): Adjusts voltage to control motor speed efficiently, offering smooth acceleration and energy savings.
- Variable Frequency Drive (VFD): Primarily used for AC low voltage motors, allows speed variation and improved energy efficiency.
- Soft Starters: Reduce inrush current during startup, minimizing mechanical stress and extending motor lifespan.
- Manual Control: Simple on/off switches or potentiometers for basic applications with minimal automation requirements.
Comparison of Low Voltage Motor Control Techniques
| Control Method | Applicable Motor Type | Key Benefits | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) | DC Motors | Precise speed control, energy efficiency, smooth operation | Robotics, automation, small appliances |
| Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) | AC Motors | Adjustable speed, reduced energy consumption, better torque control | Pumps, fans, industrial machinery |
| Soft Starters | AC and DC Motors | Reduced startup stress, lower mechanical wear, safer operation | HVAC, conveyors, electric doors |
| Manual Control | AC and DC Motors | Simple operation, low cost, easy maintenance | Household appliances, small tools |
Low Voltage Induction Motor Efficiency
Low voltage induction motors are widely used in industrial and commercial applications due to their robust construction, reliability, and relatively low maintenance requirements. One of the key considerations when selecting an induction motor is efficiency, which directly impacts energy consumption, operating cost, and environmental footprint.
Factors Affecting Efficiency
- Load Conditions: Motors operate most efficiently near their rated load. Underloading or overloading can reduce efficiency.
- Voltage Stability: Consistent supply voltage ensures optimal performance and prevents excess energy loss.
- Temperature: Excessive heat increases resistance in windings, reducing efficiency.
- Motor Design: High-quality materials, optimized winding techniques, and proper sizing improve efficiency.
Typical Efficiency Comparison
| Motor Type | Rated Voltage | Efficiency at Full Load | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Voltage Single-Phase Induction Motor | 110–240V | 65–85% | Household appliances, small pumps, fans |
| Low Voltage Three-Phase Induction Motor | 208–480V | 75–92% | Industrial machinery, conveyors, HVAC systems |
| High-Efficiency Low Voltage Motor | 208–480V | 90–95% | Energy-critical applications, commercial buildings, automation |
Improving Motor Efficiency
- Operating motors near their rated load
- Using variable frequency drives (VFDs) to adjust speed according to demand
- Ensuring regular maintenance to prevent mechanical and electrical losses
- Selecting high-efficiency designs and quality materials
Low Voltage Motor Troubleshooting Guide
Troubleshooting low voltage motors is essential to maintain performance, prevent downtime, and extend the motor’s lifespan. Common issues can arise due to electrical, mechanical, or environmental factors. Understanding how to identify and resolve these problems ensures reliable motor operation in industrial, commercial, and residential applications.
Common Faults and Causes
- Overheating: Can be caused by overloading, poor ventilation, or voltage fluctuations.
- Excessive Vibration: Often results from misalignment, worn bearings, or unbalanced loads.
- Motor Not Starting: Could be due to faulty wiring, blown fuses, or control circuit issues.
- Reduced Speed or Torque: May result from low supply voltage, mechanical obstruction, or worn components.
- Unusual Noise: Typically caused by bearing wear, loose parts, or mechanical interference.
Troubleshooting and Preventive Measures
| Problem | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting / Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Overheating | Overload, poor ventilation, voltage fluctuation | Reduce load, improve airflow, check voltage supply, ensure motor is rated for application |
| Excessive Vibration | Misalignment, worn bearings, unbalanced load | Realign motor, replace bearings, balance load |
| Motor Not Starting | Faulty wiring, blown fuses, control issues | Check and repair wiring, replace fuses, inspect control circuit |
| Reduced Speed or Torque | Low voltage, mechanical obstruction, worn components | Verify voltage, remove obstructions, replace worn parts |
| Unusual Noise | Bearing wear, loose parts, mechanical interference | Lubricate or replace bearings, tighten parts, inspect mechanical assembly |
Preventive Maintenance Tips
- Regularly inspect and clean motor components
- Ensure proper lubrication of bearings and moving parts
- Monitor voltage and current to avoid electrical stress
- Check for vibration and noise anomalies early
- Follow manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule
Low Voltage Motor Performance Testing
Performance testing of low voltage motors is essential to ensure reliability, efficiency, and safe operation. Testing evaluates key parameters such as speed, torque, current, and thermal behavior under different load conditions. Accurate performance testing helps engineers identify potential issues and optimize motor selection for specific applications.
Key Performance Parameters
- Speed (RPM): Measures the rotational velocity of the motor under rated load conditions.
- Torque: Indicates the motor’s ability to deliver mechanical power.
- Current and Voltage: Ensures the motor operates within safe electrical limits.
- Temperature Rise: Evaluates thermal performance and identifies overheating risks.
- Noise and Vibration: Assesses mechanical integrity and operational stability.
Performance Testing Table
| Motor Type | Rated Voltage | Full Load Speed | Rated Torque | Efficiency | Typical Test Focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Voltage DC Motor | 12–48V | 500–5000 RPM | 0.5–20 Nm | 70–90% | Speed regulation, torque output, thermal behavior |
| Low Voltage Single-Phase AC Motor | 110–240V | 1000–3500 RPM | 0.3–15 Nm | 65–85% | Start-up behavior, current draw, temperature rise |
| Low Voltage Three-Phase AC Motor | 208–480V | 750–3600 RPM | 5–200 Nm | 75–92% | Load response, efficiency, vibration and noise |
Future Trends in Low Voltage Motor Technology
The low voltage motor industry is evolving rapidly due to increasing demand for energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and integration with modern automation and smart systems. Engineers and manufacturers are focusing on innovative designs, materials, and control technologies to enhance performance and adaptability.
Energy-Efficient and Eco-Friendly Designs
One major trend is the development of motors with improved energy efficiency to meet global energy regulations and reduce operating costs. Lightweight materials, optimized winding techniques, and advanced magnetic components help reduce energy losses and enhance performance. Eco-friendly manufacturing processes are also being adopted to minimize environmental impact.
Integration with Smart Systems
Modern low voltage motors are increasingly integrated with IoT and monitoring systems. Sensors embedded within the motor can track temperature, vibration, speed, and torque in real-time, allowing predictive maintenance and early fault detection. This integration enhances reliability and reduces downtime in industrial, commercial, and residential applications.
Advanced Control and Automation
Future low voltage motors will leverage advanced control methods, such as adaptive PWM, sensorless vector control, and AI-based optimization. These techniques allow precise speed and torque control, improved energy efficiency, and reduced mechanical wear, supporting applications in robotics, automation, and smart appliances.
Compact and High-Power Density Motors
With increasing demand for space-saving solutions, low voltage motors are being designed to provide higher power density in smaller sizes. These compact motors can deliver strong performance while reducing weight, making them ideal for robotics, electric vehicles, and automated machinery where space is limited.
Enhanced Durability and Reliability
New materials and protective coatings are being applied to improve motor durability against heat, vibration, and mechanical stress. Enhanced insulation systems, corrosion-resistant components, and advanced bearing technologies ensure that future low voltage motors operate reliably in harsh environments.
Summary
The future of low voltage motor technology emphasizes efficiency, smart integration, compact design, and reliability. By adopting these trends, engineers can develop motors that meet the demands of modern applications while reducing energy consumption and maintenance costs. Continuous innovation in low voltage motor design will support sustainable growth across industrial, commercial, and residential sectors.
FAQ
Q1: What are the main applications of low voltage motors?
A1: Low voltage motors are widely used in industrial automation, robotics, pumps, fans, HVAC systems, electric doors, and small household appliances. They provide precise control, energy efficiency, and safe operation in both commercial and residential applications.
Q2: How can low voltage motors be maintained to ensure long-term reliability?
A2: Proper maintenance includes regular inspection, cleaning, and lubrication of moving parts, monitoring voltage and current, early detection of vibration or noise anomalies, and following recommended preventive schedules. These steps minimize downtime, improve efficiency, and extend motor lifespan.
Q3: Who is a reliable manufacturer of low voltage motors and related solutions?
A3: Shanghai Pinxing Explosion-proof Motor Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the design, research and development, manufacturing, and service of motors and motor control products. Shanghai Pinxing is a AAA manufacturer of electrical equipment in China, producing more than 1000 varieties of large and medium-sized high-voltage flameproof and increased safety explosion-proof motors, high-voltage AC motors (including asynchronous, synchronous, frequency conversion, and wound rotor motors), various types of small & medium-sized low-voltage explosion-proof motors, and AC motors. Its products are exported to more than 40 countries and regions, widely applied in coal mining, metallurgy, cement, paper making, environmental protection, petroleum, chemical, textile, road traffic, water conservancy, power, shipbuilding, and other industries. The company focuses on energy conservation, efficiency, environmental protection, integrated automation, and internationalization, aiming to provide high-quality motor products and technology solutions globally, positioning "Pinxing" as a leading motor technology solution provider and manufacturer in the international motor industry.






 English
English русский
русский Français
Français عربى
عربى